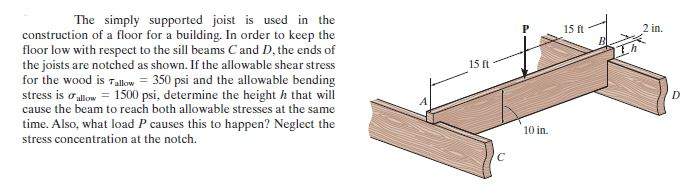
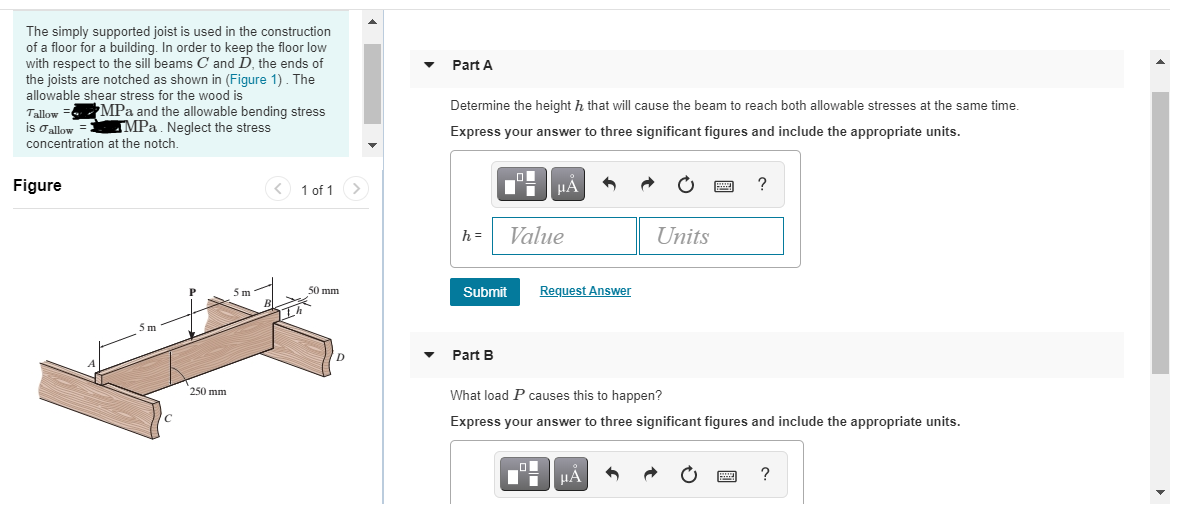
Stress Concentrations Wooden Floor Beams

This abrupt change can cause a higher stress or a lower stress by a certain factor in comparison to the nominal stress.
Stress concentrations wooden floor beams. Be suspicious of wood posts set on dirt floors or wood posts with concrete poured around the post bases. 1 composite beams bending of composite beams in the previous discussion we have considered only those beams that are fabricated from a single material such as steel. Wood with a moisture content of 19 or less is considered dry. However in engineering design there is an increasing trend to use beams fabricated from two or more materials.
Use the span tables below to determine allowable lengths of joists and rafters based on size and standard design loads. So we will have to place wood floor beams or likewise wood ceiling beams across the width of the house to support the floor joists. Common sense tells you that large floor joists can carry more load and spacing joists closer together also increases the load bearing capacity of a floor. The distance over which a wood beam bears a load when used for support is its span.
If your house is built over a basement first inspect all of the basement support beams and posts where they meet the floor. But larger is not always better when builders are constructing a home or adding a room addition. Beam depth h0 can be calculated for comparison with that given by the design criteria. The strength of wood increases with a reduction in the moisture content.
A good analogy for stress concentrations is a river. Stress concentrations are deviations from the nominal stress on a part. 9 1 and 9 2 and this. Tapered beams deflect as a result of shear deflection in ad dition to bending deflections figs.
Reference design values for sawn lumber assume maximum moisture content of 19. 4 3 6 3 for beams of circular cross section with a diameter greater than 13 5 or for 12 or larger square beams loaded in the plane of the diagonal the size fac tor shall be determined in accordance with 4 3 6 2 on the basis of an equivalent conventionally loaded square beam of the same cross sectional area. You can also use the wood beam calculator from the american wood council website to determine maximum rafter and joist lengths. The span of any wood beam depends on many factors such as type of wood weight of the load and overall size of the beam.
Kiln dried or seasoned wood would be considered dry as long as it hasn t been exposed to weather long enough to cause re saturation. The floor joists are still 12 long but now you can see a floor beam running horizontally across the middle of the house supported by the lower. Calculating the span of a beam requires using various factors that you need to first determine for a structure. The extra two inches of vertical distance when a floor is framed with 2 x 10 joists rather than 2 x 12s can be quite important for example.
What causes a stress concentration is an abrupt change in the flow of stress through a part. Conversely the deflection of a beam can be calculated if the value of the abscissa is known.