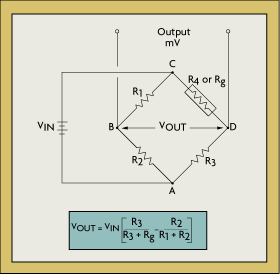
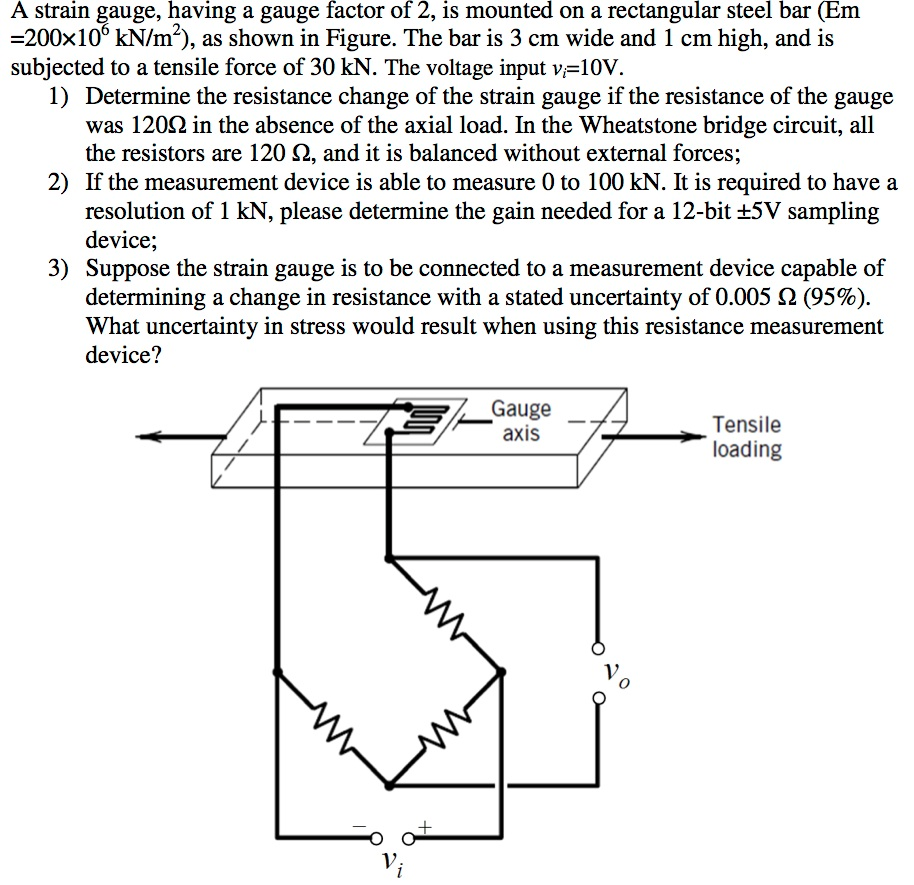
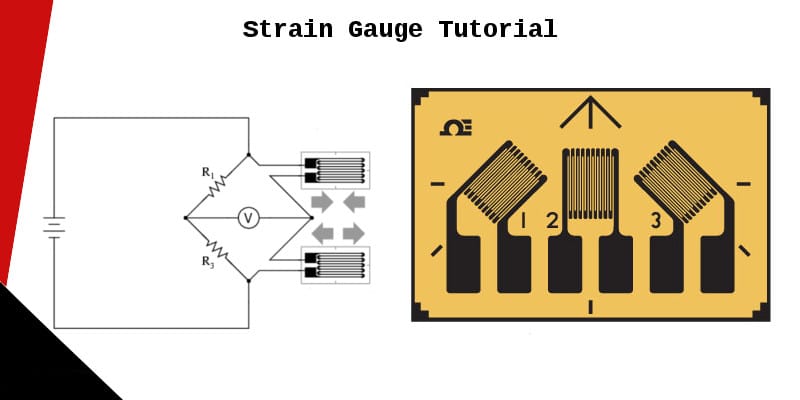
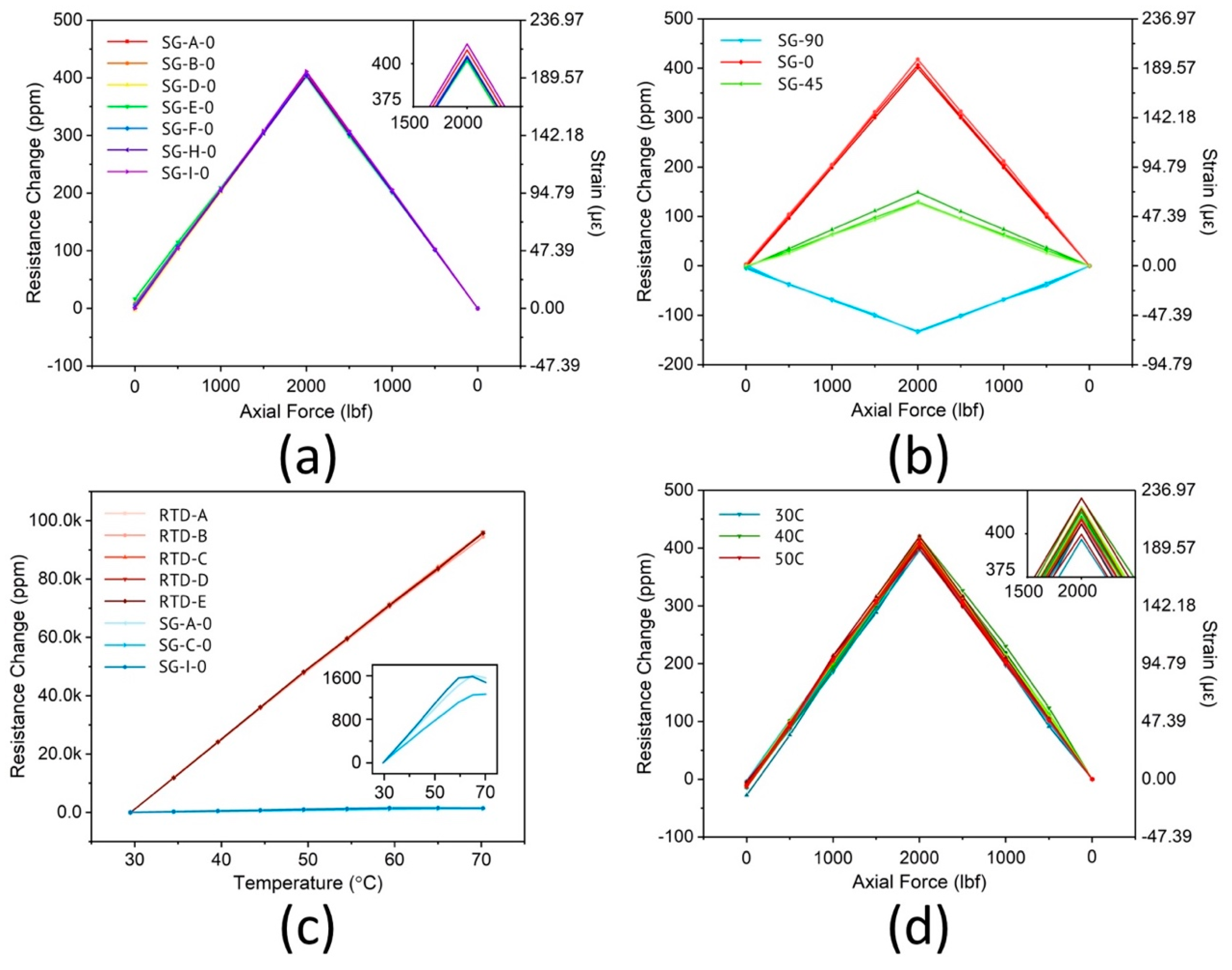
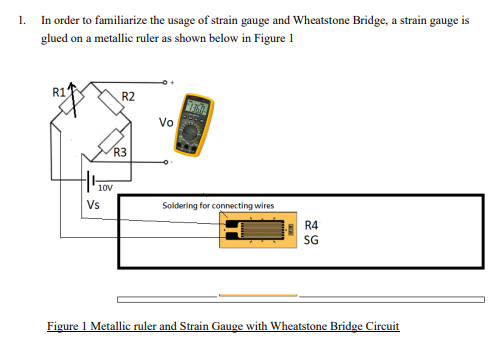
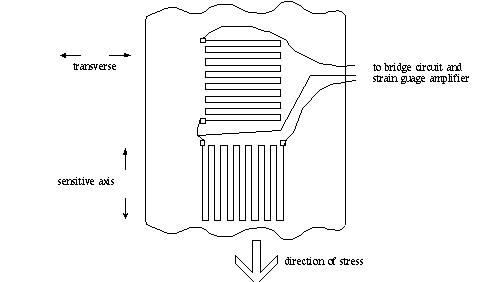
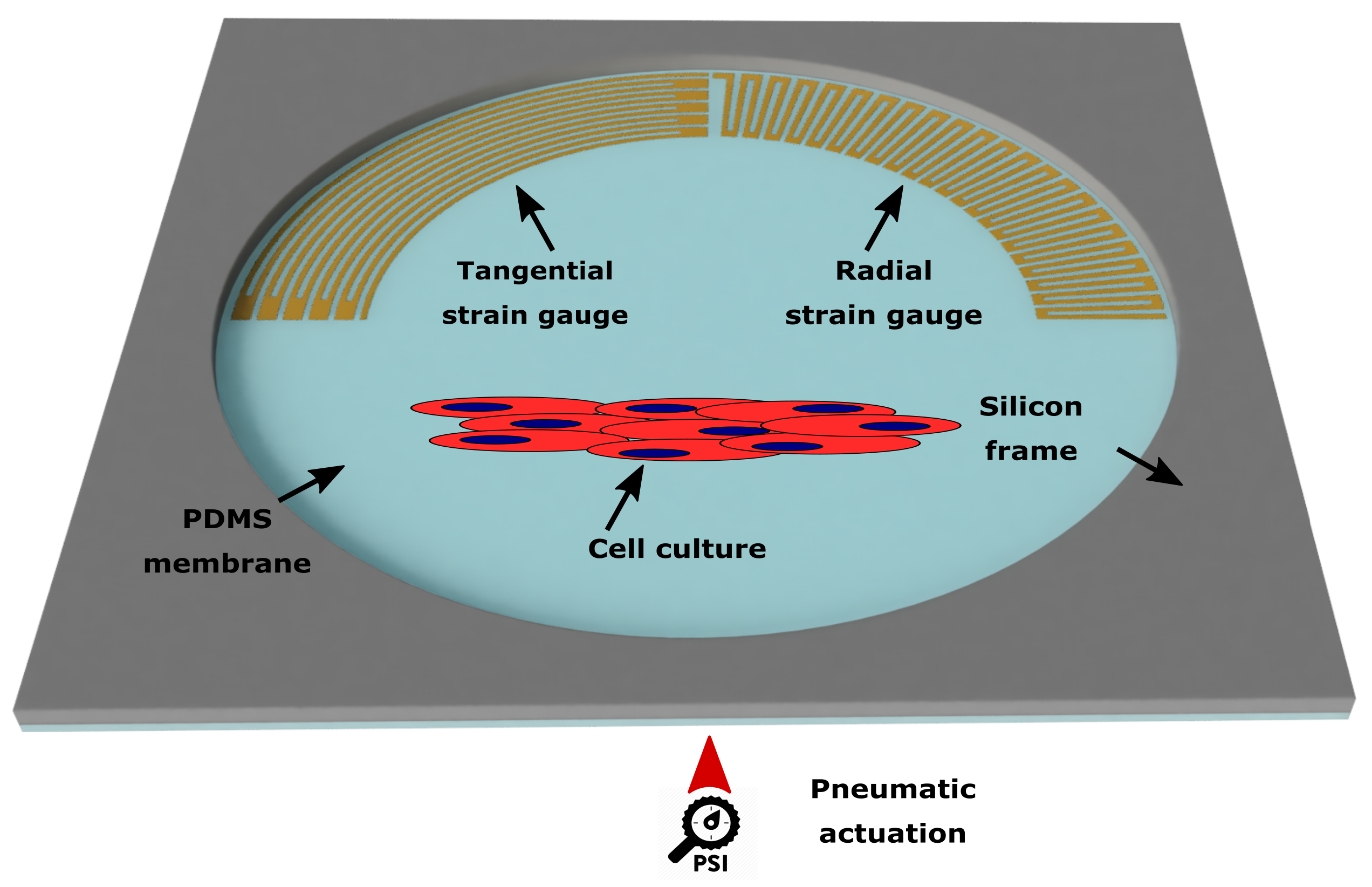
Strain Gauge Mathematics

When a load is applied to the surface.
Strain gauge mathematics. Mechanical strain gauges are among the most straightforward in the way of making and measuring. The method of measurement consists of measuring the elongation of the blades and reading this value on a scale magnified 1000 times transmitted by means of mechanical levers. The latter form of the strain gauge is represented in the previous illustration. Bonded foil strain gauges the first bonded metallic wire type strain gauge was developed in 1938.
A strain gauge s conductors are very thin. Invented by edward e. Ruge in 1938 the most common type of strain gauge consists of an insulating flexible backing which supports a metallic foil pattern. If made of round wire about 1 1000 inch in diameter.
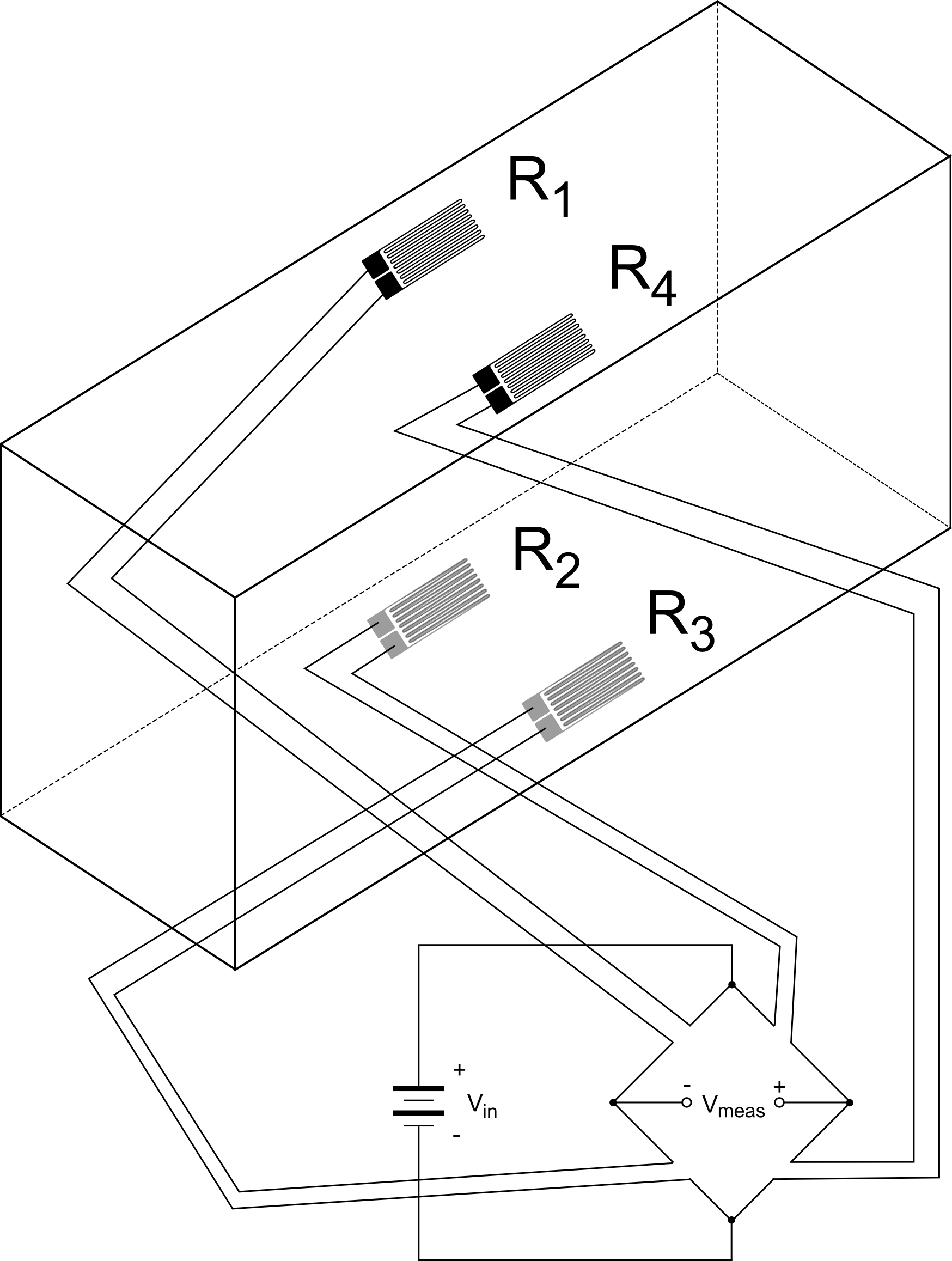
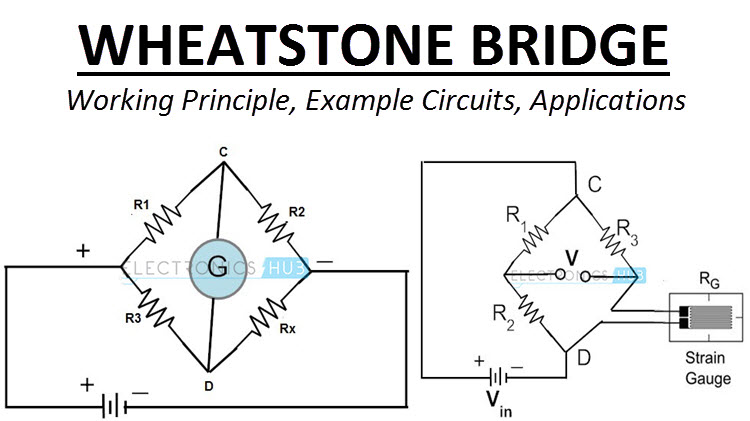
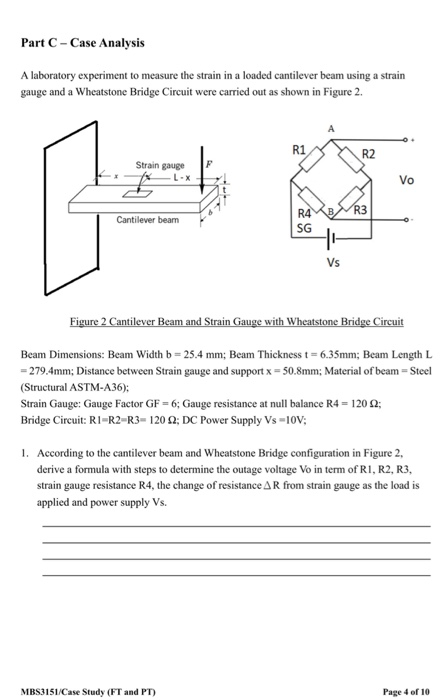
Strain gauge is a passive transducer that converts a mechanical elongation or displacement produced due to a force into its corresponding change in resistance r inductance l or capacitance c. Simmons and arthur c. A strain gauge also spelled strain gage is a device used to measure strain on an object. If a metal piece is subjected to a tensile stress the metal length will increase and thus will increase the electrical resistance.
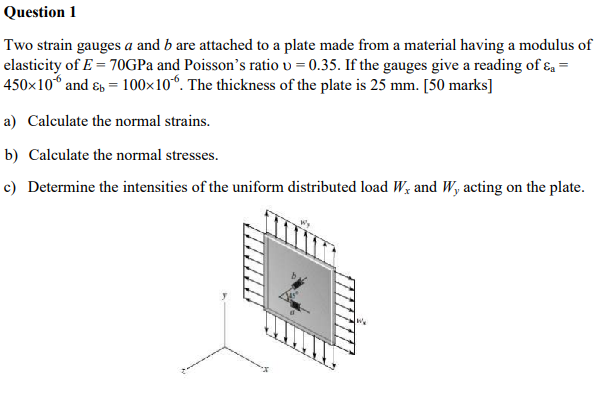
0 025 mm thickness bonded directly to the strained surface by a thin layer of epoxy resin. A strain gauge is basically used to measure the strain in a work piece. The metallic foil type strain gauge consists of a grid of wire filament a resistor of approximately 0 001 in. The rosettes mathematics plugin is used to calculate the plane strain and plane stress state measured by strain gauges in common strain rosette patterns.
As the object is deformed the foil is. The gauge is attached to the object by a suitable adhesive such as cyanoacrylate.